Alphabet’s Project ‘Malta’ To Develop Energy-storage System Using Salt And Hydrogen Liquid
Short Bytes: Alphabet Inc’s secretive Lab X is developing an energy storage system. The system will have four tanks; two filled with salt and the other two with hydrogen liquid and antifreeze. Salt maintains temperature, therefore, the system can hold energy for more hours and days. Most importantly it runs at low temperature and does not require expensive materials.
Alphabet Inc.’s research laboratory X is developing a system that can store renewable energy. As described by the researchers, this system can be established anywhere. Also, it can beat lithium-ion battery in terms of battery life.This is a Moonshot project like Google Glass that is looking forward to developing energy-storage systems.
Also Read: Google Parent Alphabet Beats Apple To Become The Most Valuable Company In The World
Obi Felten, a director at X shared that if Moonshot aims to solve big problems like climate change, it can earn them a lot of profit in the market. Because climate issue is one such serious problem that never gets solved.
Alphabet’s X is coming to the market that has a scope of about $40 billion of investments by 2024, as per Bloomberg New Energy Finance. Last year, nearly 790 megawatts of energy was stored, and in the coming 7 years, the capacity is expected to reach 45 gigawatts.
A large amount of energy gets wasted due to lack of energy-storage systems. Right in the first half of this year, California wasted about 300,000 megawatts of energy.
Also, Felten is majorly interested in working with companies in China which is a hefty consumer of energy and also a country where almost all Google services are banned.
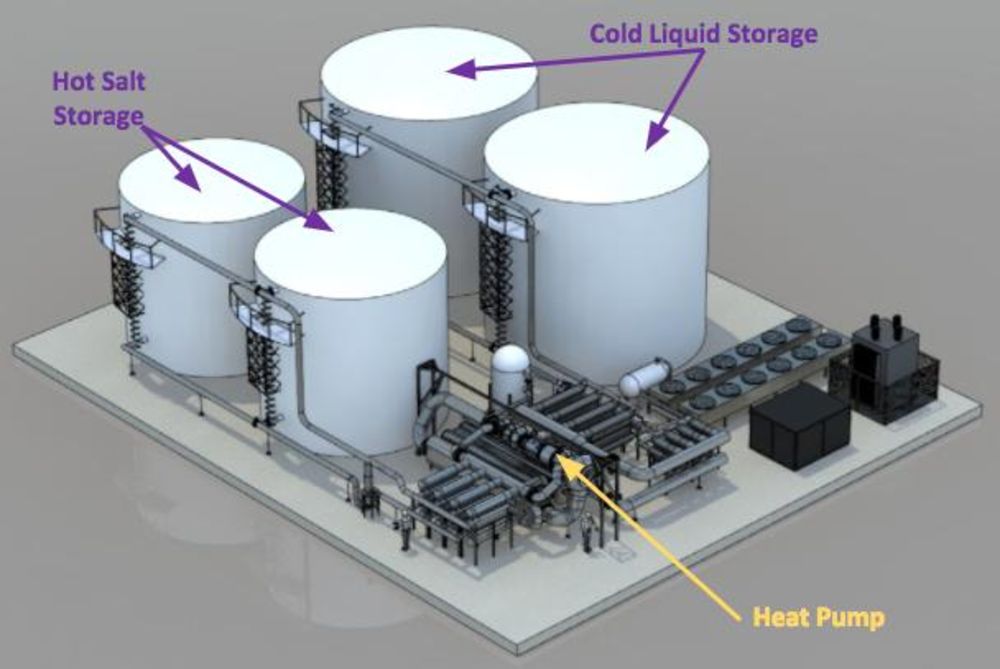
As reported by Bloomberg News, the system has four cylindrical tanks connected via pipes to a heat pump. Two of them are filled with Salt and the other two are filled with antifreeze or hydrocarbon liquid.
The energy in the form of electricity is taken in by the system and separated into two streams of hot and cold air. After that, the hot air heats up the salt and the cold air cools the antifreeze. This energy can later be consumed by the reversal process when the hot and cold air combines pushing the turbines with the air surge.
The salt helps to maintain the temperature, thus allowing the system to store energy for long and more hours. The system runs at lower temperatures and does not require expensive ceramics and steels.
“Think of this, at a very simple level, as a fridge and a jet,” said Julian Green the product manager for Malta.
The system is a big step towards the thought of energy conservation, something of sustainable development.
Read the full story here.
Also Read: Get Electricity From Solar Energy-harvesting 3D Printed ” Trees”