What Is A VPN? How VPN Works & Why You Need One?

A Virtual Private Network or VPN is an encrypted connection that protects your internet connection and privacy online. It does so by creating an encrypted tunnel that transfers your data. While using a VPN service, it hides your real IP address and keeps you safe on public networks.
Usually, Virtual Private Network technology is used to set up a private network over the internet to share the resources of a corporate intranet with remote users and other office locations of the company. People can also use VPN to access their home network remotely.
A VPN is like your private lounge on the internet, where you can hang out without interference from other people. Some of the popular paid VPNs are PIA, ExpressVPN, and others. They allow access to your home network or the corporate network of your company, even if you’re in some other corner of the world.
Popular VPN Services
NordVPN, Express VPN, and Private Internet Access, all these are popular for the QoS and security they provide in their private/ secure connections.
Cyber Ghost, Surf Easy, and Tunnel Bear are some free VPN services you can use if you want to save money. But you’ll have to satisfy yourself with fewer features, download limits, or advertisements. Also, these free services can’t beat the paid services. Note that. Also, check out our detailed guide on black friday VPN deals for 2021 here!
How does a VPN work?
The working principle of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is not a terrible deal to understand, though it is. Before that, you need to understand the set of rules used in providing a secure personal network.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)/TLS (Transport Layer Security): It uses a 3-way handshake method for assuring proper authentication between the client and server machines. The authentication process is based on cryptography, where certificates, behaving as cryptographic keys already stored on the client and server sides, are used for initiating the connection.
IPSec (IP Security): This protocol can work in transport mode or tunneling mode to do its job of securing the Virtual Network connection. The two modes differ because the transport mode only encrypts the payload in the data, i.e., only the message present in the data. On the other hand, the tunneling mode encrypts the entire data transmitted.
PPTP (Point-To-Point Transfer Protocol): It connects a user located at some remote location with a private server in a VPN network and also uses the tunneling mode for its operations. Low maintenance and simple working make PPTP a widely adopted VPN protocol. Further credit goes to the inbuilt support provided by Microsoft Windows.
L2TP (Layer Two Tunnelling Protocol): It facilitates the tunneling of data between two geographical sites over the VPN network, often used in combination with the IPSec protocol, which further aids the security layer of the communication.
You now have a rough idea about the various protocols used in a VPN. We shall proceed further and see how it works. When you connect to a public network, for example, free WiFi networks at airports, you can assume that all your data is flowing through a big tunnel along with the data of other users.
Anyone who wants to spy on you can easily sniff your data packets from the network. When VPN comes into the scene, it provides you with a secret tunnel inside that big tunnel. In other words, all your data transforms into garbage values so that no one can recognize it. Also, check out our detailed article on the best open source VPN that you can use in 2022 here!
Why do you need a VPN service?
Surfing the web or making transactions online on an unsecured network means you could be exposing your private information. Hence, to be safe, a VPN should be a must for everyone who wishes to keep their information secure.
For instance, if you’re at a public place and using their WiFi, you are at risk of exposing your sensitive information while surfing the internet. Users on the same network could access any data transmitted over it.
By using a VPN, your data stays encrypted and anonymous, locking out any third parties involved.
How a VPN protects you online
As explained above, a VPN encrypts your data so you can remain anonymous from any trackers or eavesdroppers online. By using a VPN, nobody can access what you do on public networks and home networks.
Encryption is the best way to remain anonymous online, and data privacy is a major concern as well.
Setting up a VPN Connection involves Three Phases
Authentication: In this step, data packets are first encapsulated, basically wrapped inside another packet along with some headers, and other stuff attaches. All of this conceals the identity of the data packets. Now, your device initiates the connection by sending a Hello request to the VPN server, which replies with an acknowledgment and asks for the user credentials to verify the authenticity of the user.
Tunneling: After the authentication phase completes, what we can say, an imaginary tunnel is created, which provides a direct point-to-point connection through the internet. We can send whatever data we want to via that tunnel.
Encryption: After we’ve successfully created the tunnel, it can transfer whatever information we want to, but that information is still not safe if we use a free VPN service. That’s because other people also use it. So, we encrypt the data packets before sending them over the tunnel, thus, barring any other user from peeping into our packets. They will only see some unrecognizable rubbish data flowing through the tunnel.
Now, if you want to access a website, your device will send the access request to the VPN server, which will then forward the request to the website in its name and receive the data from it. Then, the website will transmit this data to your device. The website will think that the Virtual Private Network server is the user. It will find no trace of you or your device as the actual user unless you transmit some personal information over the connection. For example, your identity will reveal if you access a social networking website like Facebook or Twitter using a VPN connection.
Uses of VPN: What does a VPN do?
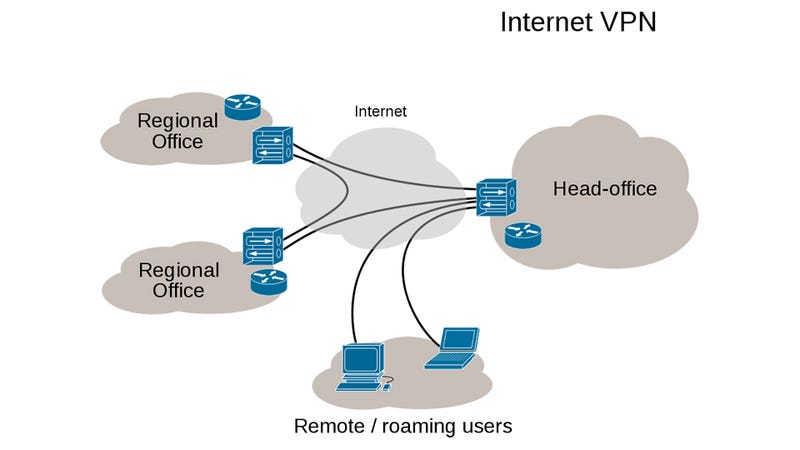
A VPN connection provides direct access to a corporate network to a user who is not in the geographical coverage of the network. Logically, the remote user is connected just like a regular user sitting inside the campus of a corporate organization.
It also has a use of providing homogenous network environments to a corporate firm having its office locations across the world. Thus, creating an uninterrupted sharing of resources bypassing the geographical hurdles.
Other uses of VPN include accessing services on the internet that are not available in a particular country or region, accessing censored content, or if a user only wants to remain anonymous on the web.
VPN on Android and iOS
You can also set up a VPN connection on your smartphone running Android OS. It allows you to access your company’s private network right on your Android device. VPN also facilitates a network administrator to control your device, add or delete data, and track your usage.
Also Read: 7 Best Free VPN Apps For Android
Same way, Apple devices, including iPhone (iOS) and iPad (iPadOS), come with built-in support for virtual private networks. You can visit the Settings app and create a new VPN profile using the credentials given by your VPN provider.
Types of VPN
Mainly, VPNs are of two kinds, namely, Remote Access Virtual networks and Site-to-Site VPN. The second kind, site-to-site virtual private networks, have further sub-types.
Remote Access VPN
When we talk about Remote Access VPN, we are talking about giving someone access to an existing private network over the internet. The private network can be a network set up by some corporate organization equipped with database and network hardware related to the organization or any project.
Because of remote access VPN, there is no need for an employee to connect to his company’s network directly. He can do so with the help of the necessary VPN client software and credentials given by the firm.
Remote Access VPNs aren’t the buzzwords for the corporate sector only; home users can also leverage them. For instance, you can set up a virtual private network at your home and use the credentials to access it from somewhere else. This way, the websites you visit will see the IP address of your home network rather than your actual IP address.
Moreover, most VPN services you see in the market are examples of remote access VPN. These services mainly help people eliminate geographical restrictions on the internet. These limitations are probably there because of government-led blocking or if a website or service is not accessible in a particular region.
Site-to-Site VPN
The word ‘site,’ in this case, refers to the physical location where a private network exists. It also has a name of LAN-to-LAN or Router-to-Router VPN. In this type, two or more private networks in different parts of the world are inter-connected, all serving as one single virtual private network on the internet. Now, there are two sub-kinds of site-to-site virtual private networks.
Intranet Site-to-Site VPN
We call it intranet site-to-site VPN when different private networks of a single organization are clubbed together over the internet. This type of VPN can share resources across various office locations of the company. One other possible way would be laying out separate cables across different office locations, but that won’t be feasible and might incur high costs.
Extranet Site-to-Site VPN
There can be a need to connect the corporate networks belonging to different organizations. They might be collaborating on a project involving resources from both organizations. Such virtual private networks created are known as extranet site-to-site VPNs.
Pros and Cons
The biggest advantage of using a VPN is it provides a cost-effective way to create a single private network in comparison to using separate leased lines that can burn the pockets of corporate firms. All credited goes to the internet, for acting as the medium for uninterrupted VPN connections.
Apart from all the right things VPN does for us, it has its weak sides too. Not having a streamlined procedure for ensuring Quality of Service (QoS) over the internet is VPN technology’s biggest incapacity. Furthermore, the level of security and authenticity outside the private network is beyond the purview of VPN technology. The incompatibility between different vendors only adds to its bunch of drawbacks.
What you should look for in a VPN
It entirely depends on what you actually use a virtual private network for. Before selecting a provider, ask yourself three questions: How fast is it? Will it keep my data safe? Will it respect my privacy? Likewise, these are the major factors you should look for while selecting a VPN provider.
Winding Up
VPN has so far equipped us with an extraordinary level of security and anonymity. As a result, we can accomplish while sharing our confidential data over the internet. Corporate giants have always admired the ease and uniformity they can engineer in their network using a VPN. Though it has its limitations, Virtual Private Network has outperformed our expectations. We should praise the Private Network technology for the cost-effectiveness it provides in its operations.
So, this is everything about Virtual Private Network, what it does, and how it works to protect our data. If you have something to add about the VPN technology, feel free to drop your thoughts in the comments.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is a service that helps you keep your data and privacy online in safe hands.
Yes, using a virtual private network from a trusted provider is completely safe.
It is legal to use a virtual private network while browsing the internet.