LTE (4G) Flaw Allows Attackers To Redirect Browsers And Spy On You
The Long Term Evolution (LTE) standard for mobile communication, also known as 4G was designed to overcome security flaws of its predecessor standards and is used by millions of people across the globe.
However, researchers have now uncovered weaknesses in LTE that allows attackers to hijack browsing session which redirects users to malicious websites and spy on their online activity to find out which sites they visit through their LTE device.
They described three methods of attacking the data link layer of the LTE network on their website. The first two are passive attacks that perform identity mapping and website fingerprinting. However, the most intrusive one is the third attack termed ‘aLTEr’ by the team.
What is aLTEr?
‘aLTEr’ is an active attack which abuses the data link layer of LTE. It allows attackers to intercept users’ browsing session and also redirect network requests via DNS spoofing.
How does aLTEr work?
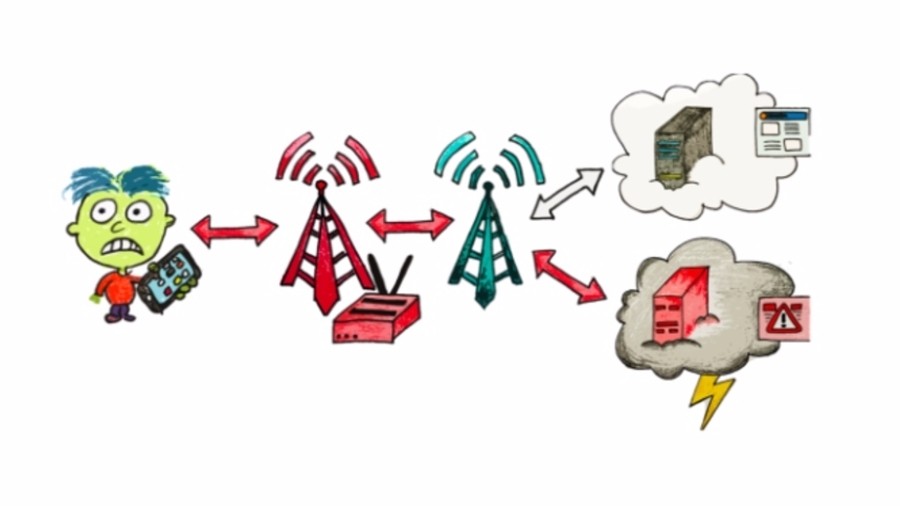
According to the researchers, this attack the data layer of LTE network is not integrity-protected. So ‘aLTEr’ pretends to be the real user it wants to attack by creating a cell tower.
This fake cell tower can take requests from the user and pass on to a real cell tower, but before forwarding, it alters the bits of the encrypted packet. Later the attacker can decrypt that packet and re-encrypt it with a new DNS server to redirect it to malicious websites.
How feasible is aLTEr?
This method has limitations such as it requires an equipment setup worth $4000 to operate and it the LTE device must be within a 1-mile radius of the attacker to work.
So the good news is that conducting an aLTEr attack in real-world scenarios is quite difficult. However, it doesn’t eliminate the fact that aLter is very much real and feasible for someone with the right resources.
What makes it worse is the fact that this security flaw cannot be patched as it this weakness is built into the LTE standard itself.
How to prevent aLTEr?
The simplest way to avoid being a victim of aLTer is through the use of HTTPS. Always remember to check the “Secure” text mentioned beside the address bar and avoid trusting a website labeled as “Not Secure” by your browser.
Also Read: Gentoo Linux Distro Hacked: All Code On GitHub Compromised