This Sensitivity Map Shows The Most Vulnerable Places On Earth


Short Bytes: To identify the biggest climate change risks, researchers have created a vegetation sensitivity index map that shows the most vulnerable places on Earth. Using different data obtained from satellites, this map depicts the places that need more attention.
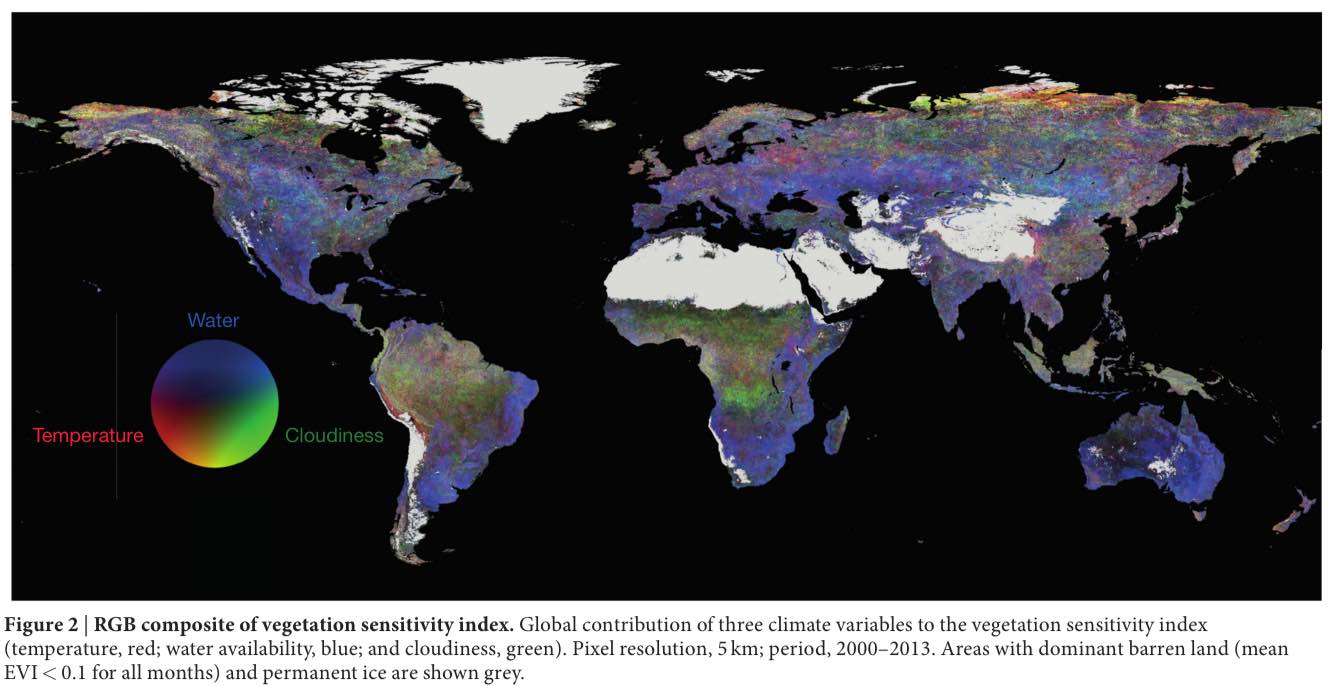
To reveal the most vulnerable parts of Earth, the researchers have prepared a map using a new system to analyze the satellite data. Published in Nature, this map depicts a vegetation sensitivity index (VSI) which is basically the plant cover on the ground per year, created using satellite-based moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer.
VSI is a new way to predict the future fluctuations in vital indicators like temperature, cloud cover, and moisture. This helps us to study the water availability changes, rainfall predictions, weather changes etc. The same could be seen in the map below where three climate variables contribute to the vegetation sensitivity index.
Here, the areas with dominant barren land and permanent ice are shown grey. On the other hand, the contribution of climate change variables is shown in the following color scheme: Temperature – Red, Water availability – Blue, Cloudiness – Green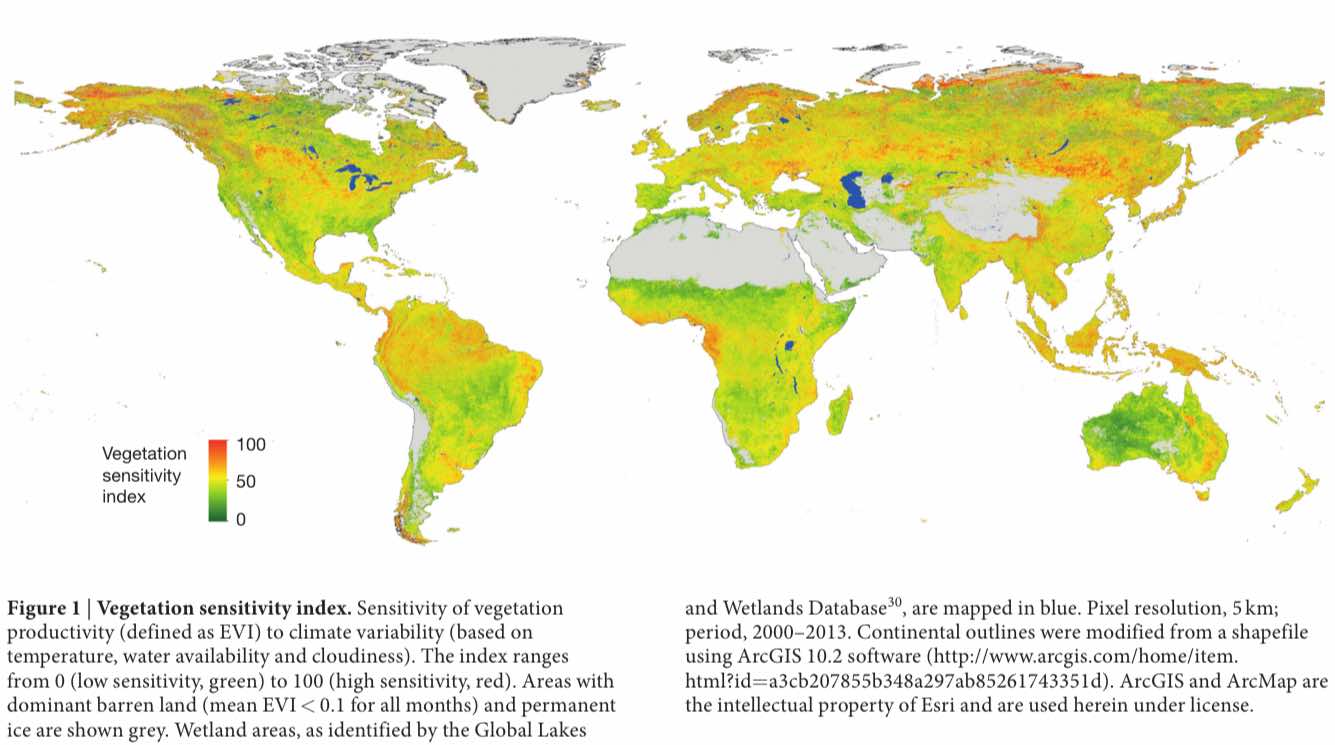
In Nature, the researchers explain further:
It should be noted that these aren’t the areas that are on the verge of destruction. The researchers have called them as the areas with “lower resilience and with a high chance of crossing the threshold.”
For more, you can read this publication in Nature.
Also read: This Map Shows The Creepy Satellites Passing Above Your Home In Real Time






