All You Need To Know About Different Types Of USB Connectors And Cables

With each generation, USB ports and cables have blessed us with faster data transfer speeds, and compact lightweight form factors. Keeping that in mind, let’s talk about all you should know about the different types of USB connectors, their speeds, uses, how to identify a USB from a logo, and much more.
While many of us already have a basic awareness of what USB ports and connectors are, we won’t be going into the part where we explain what a USB connector and a port are. Instead, in this article, as told earlier, we’ll talk about the form factors of different types of USBs, their data transfer speeds, and the color-coding of USB ports to help you identify the type of USB port and its basic specifications.
Types of USB connectors (Form Factor)
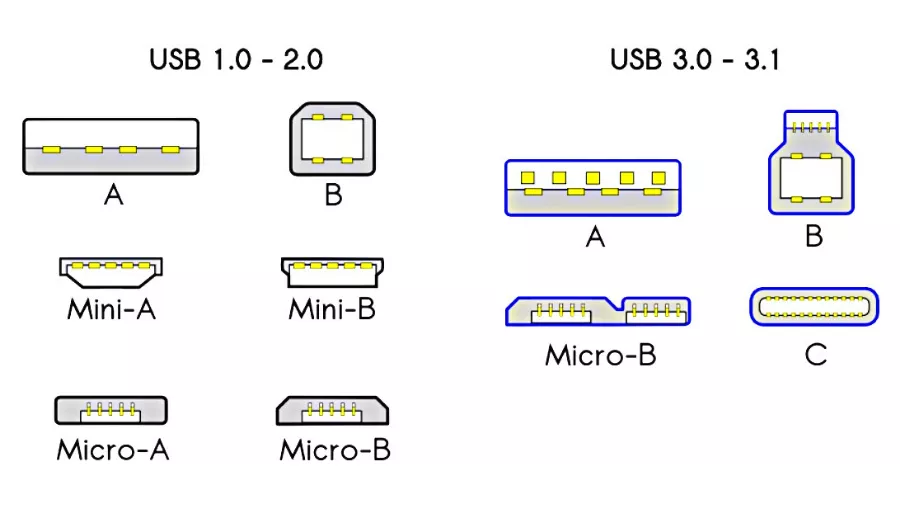
USB Type-A
USB Type A is the original rectangular connector that is found on one side of almost all USB cables. While they’ve been with us since the invention of USB, no one really figured out how to connect it in one go (pun intended). In addition, USB A can be found on almost all the gadgets nowadays, be it a laptop, a console, media players, TVs, etc.
Furthermore, the USB A is currently functioning on two generations, USB 2.0 and USB 3.x; and while the USB 3.x cable will work on a USB 2.0 port, the transfer speeds will remain that of USB 2.0. In addition, if you connect a USB 2.0 to a USB 1.1 port, the data transfer speeds will be that of the older generation.
USB Type-B
You won’t be seeing these USBs in your everyday life since the USB Type-B is confined to printers, external hard drives, and computer systems. That being said, USB Type-B also has two different generations; one is the USB 2.0, and the other is the USB 3.0. To be precise, USB Type-B is only used on large electronic devices and is almost the shape of a square.
Mini USB-B
Those of you who’re into photography might be familiar with the Mini USB-B. This USB connector is generally found on digital cameras and some older generations of handheld music players. As the name suggests, it is a mini version of USB Type-B and only has generations 1.1 and 2.0 speeds with 4 or 5 pin connectors.
Micro USB-B
If you rewind back to the previous decade, Micro USB-B or more commonly known as Micro USB was the standard for most electronic gadgets, from smartphones to music players to Android tablets. Micro USB-B or Micro USB is able to charge the gadget and provide data transfer. While it is no longer the standard USB, you might find one every now or then since most manufacturers opt for a USB Type-B owing to its lower price.
USB Type-C or USB-C
The latest generation of USB connectors is the USB Type-C; you’ll find this on virtually all Android tablets and smartphones nowadays, and even on the iPad. Not only does the Type-C provides for data transfer and charging, but it also puts display connectivity on the table.
One big USP here is that USB-C is a reversible connector unlike B and A, which means you plug in either way. This is similar to what we see in the case of Apple’s Lightning Connector. From smartphones to Android tablets, game controllers to music players, laptops, and wireless earbuds cases, Type-C is everywhere to be found.
Since the Type-C offers great data speeds and a smaller form factor, plus you only need to keep one USB Type-C cable for all your gadgets. A salient feature called Alternate Mode makes USB-C a truly universal connector. With Alt mode, a single USB-C port can provide access to other interfaces like Thunderbolt, HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.
Given that, USB C is able to achieve what other USBs have not, apart from being the universal USB port, this connector can even feed today’s power-hungry devices, that too at blazing fast speeds.
USB color coding
| Color | Type | USB Specification | Misc information |
| White | USB A, Micro USB A, or USB B | USB 1.0 generations | |
| Black | USB A, USB B, or Micro USB B | USB 2.0 | |
| Blue | USB A or USB B | USB 3.0 | |
| Teal | USB A or USB B | USB 3.1 Gen 1 | |
| Red | USB A (Sleep and Charge) | USB 3.1 Gen 2 USB 3.2 | Sleep and Charge means the USB port will remain active even if the PC is powered down |
| Yellow | USB A (Sleep and Charge) | USB 2.0 USB 3.0 | |
| Orange | USB A (Sleep and Charge) | USB 3.0 | Capable of charging |
Data transfer speeds
Since the USBs come in all shapes and sizes, their functionality also differs, along with the different rates at which they transfer data. Moreover, keep in mind while purchasing a USB cable that some cables only support data transfer and do not support charging. With that in mind, let’s see the different USB types and their data transfer speeds.
First off, USB 1.1 has the lowest data transfer speeds of the lot, with speeds up to only 1.5 Mbps, which is pretty sluggish in accordance with today’s standards. That being said, you won’t find many devices that come with a USB 1.1 connector inbuilt. Coming to USB 2.0, which is still somewhat common in today’s times, has data transfer speeds of up to 12 Mbps. Moreover, USB 2.0 also has a high-speed version that can handle data transfer speeds of up to 480 Mbps.
Coming to USB 3.0, it sports data transfer speeds of up to 5-20 Gbps, depending on the version. Now, the latest generation of USBs, USB 4.0 is the one that will give you blazing-fast data transfer speeds. USB 4.0 Gen 3×2 offers data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps, which is similar to Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4.
An important thing here is that USB 4.0 only works with Type-C ports although you can plug in an adapter to use other connectors. Support for USB-PD (Power Delivery) is also a must in the case of USB4.
Types of USB standards
| USB Standard | Logo | Connector types | Max. data speeds |
| USB 1.1 | USB A USB B | 12 Mbps | |
| USB 2.0 |  | USB A USB B Micro USB A Micro USB B Mini USB A Mini USB B USB C | 480 Mbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 |  | USB A USB B Micro USB B USB C | 5 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 |  | USB A USB B Micro USB B USB C | 10 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 (Gen 2×2) | 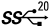 | USB C | 20 Gbps |
| USB 4 (Gen 2×2) |  | USB C | 20 Gbps |
| USB 4 (Gen 3×2) | USB C | 40 Gbps |
Types of USB: Wrapping up
Now with all the basic information out of the way we’re hopeful about contributing some towards your better understanding of different types of USB ports and their uses. Meanwhile, if there’s any information you’d like us to add to the above information, do let us know in the comments.






