Piton: An Open Source Processor That Can Power A 200,000-core Computer

Short Bytes: The researchers at Princeton University have developed an open source chip named Piton. This 25-core chip is highly scalable. The researchers aim to build a 200,000-core computer using 8,000 Piton chips. Piton is made to address data centers’ specific requirements like high speed and low energy consumption.
A group of researchers at Princeton University has developed a new computer chip that claims to boost the performance of data centers. Unarguably, these massive centers power today’s internet. The researchers have built a chip specifically to address the needs of these servers.
Named Piton, after the metal spikes used to easily climb mountains, this chip was presented at Hot Chips, a symposium on high-performance chips, on August 23.
Piton could effectively reduce the energy usage while boosting the processing speed. Thanks to its scalable architecture, designs ranging from a dozen to several thousand cores can be built. The developers of Piton wish to build an insane 200,000-c0re computer powered by 8,000 64-bit Piton chips.
Piton is an open source processor
Based on the OpenSparc design, which is a modified version of Oracle’s OpenSpart T1 processor, Piton is an open source chip. Oracle uses Sparc in its high-end database servers.
Lately, there have been some interesting developments in the world of open source processors. A popular architecture that’s gaining attention is RISC-V, which is being used to develop a new open source chip. The Open Core Foundation is also working to release an open source architecture for the SH2 chip.
Coming back to Piton, it has 25 cores, each one operating at 1GHz, arranged in five lines. Each core has 64KB of L2 cache, that gives us 1.6MB cache for one chip. For fast communication with other cores, there’s a mini router in other cores. For large-scale parallel computing, each core comes with a floating point unit.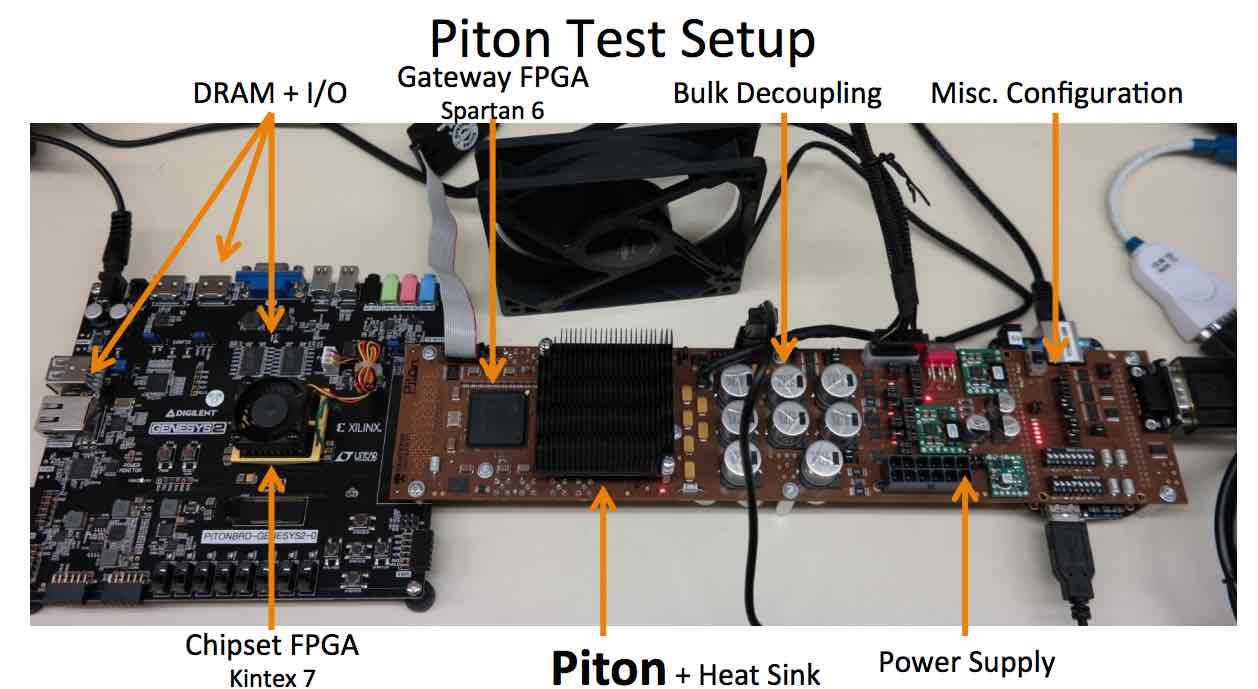
The researchers claim that Piton is the largest processor in academia. This claim is supported by the 460 million transistors in Piton. If we consider chip cores as the criteria, a 1,000 core chip called KiloCore has been developed by the researchers at University of California, Davis.
Here’s what David Wentzlaff, a Princeton assistant professor, has to say about Piton:
Source: Princeton.edu
Did you find this article interesting? Don’t forget to drop your feedback in the comments section below.
Also Read: Google, HP, Oracle Join RISC-V To Make Open Source Processor Core