CAMM2 RAM Standard: Everything You Need To Know About It
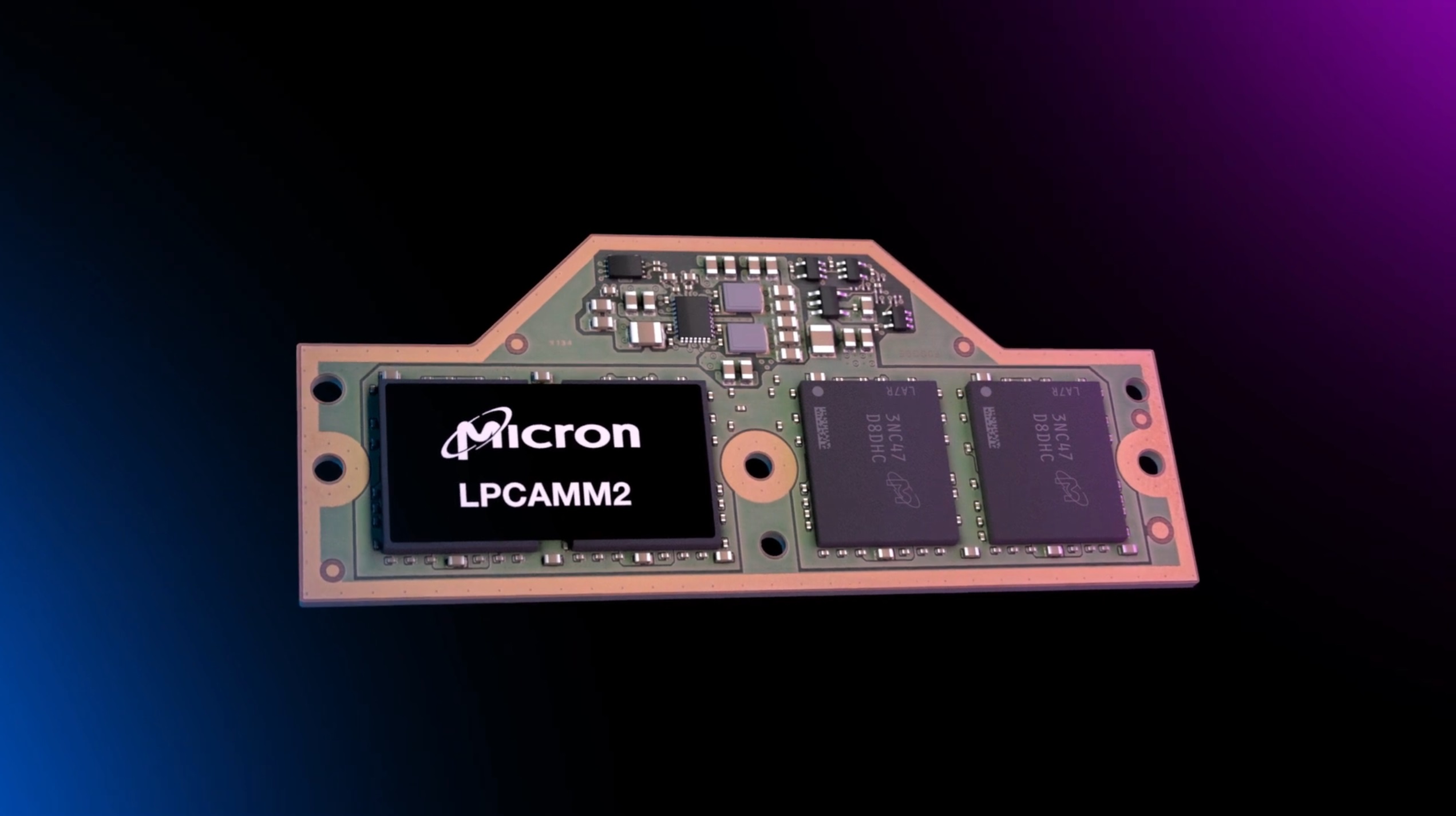
RAM is perhaps one of the most crucial aspects of a computer, as it stores all ongoing tasks and processes. Given its importance, one might assume that the tech industry consistently updates the RAM standard to make it faster and more stable. Unfortunately, this is not the case, as the SO-DIMM has been the industry standard for over 25 years. However, the memory standards organization JEDEC has agreed upon a new Compression Attached Memory Module (CAMM2) RAM standard. Here is everything you need to know about it.
The need for a new standard
To understand the need, we must first examine how SO-DIMM memory works. When a processor wants to store information, it sends the data to the RAM, which then stores it on specific chips. However, the distance between the RAM and the processor plays a significant role in the process. The longer the distance, the greater the signal loss and integrity. This means that the regular SO-DIMM slots, typically sitting 7 cm away from the processor, are at a significant disadvantage compared to soldered memory, which sits closer to 1 cm.
As a result, SO-DIMM memory is inherently slower than soldered memory. Moreover, considering the fact that SO-DIMM has a maximum speed of 6,400MHz means that it won’t be able to handle the DDR6 standard, which is already in the works.
Advantages of CAMM2
The new standard comes in two variants: CAMM2, featuring Double-Data-Rate (DDR) memory chips, and LPCAMM2, equipped with Low-Power Double-Data-Rate (LPDDR) memory. Talking about the advantages, the flat and wider design of CAMM2 results in a significantly lower Z-height compared to conventional SO-DIMM RAM modules. This allows laptop makers to integrate additional components or allocate space for larger heatsinks and better cooling systems.
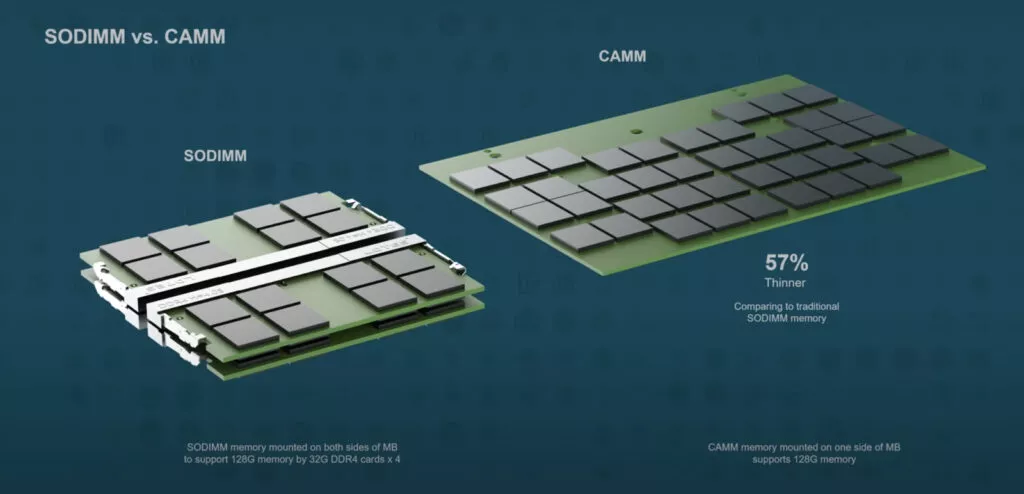
Additionally, CAMM2 supports higher memory capacity on a single module and can be installed approximately 50% closer to the CPU. This proximity allows for higher data rates and lower latency without the need for soldering memory chips to the motherboard. While the exact data rates will differ for each manufacturer, Micron claims that LPDDR5X CAMM2 can achieve an impressive 9600 MT/s transfer rate.
Furthermore, the memory standard consumes significantly less power than its predecessor, meaning that users can also expect some amount of battery gain.
Difference between CAMM2 and LPCAMM2
Although both standards share the same name and connector, they have different pinouts, mounting procedures, and designs. This is because LPCAMM2 modules are tailored for thin and light laptops as well as handheld PCs, while CAMM2 is geared towards high-end gaming laptops.
When can we see CAMM on laptops?
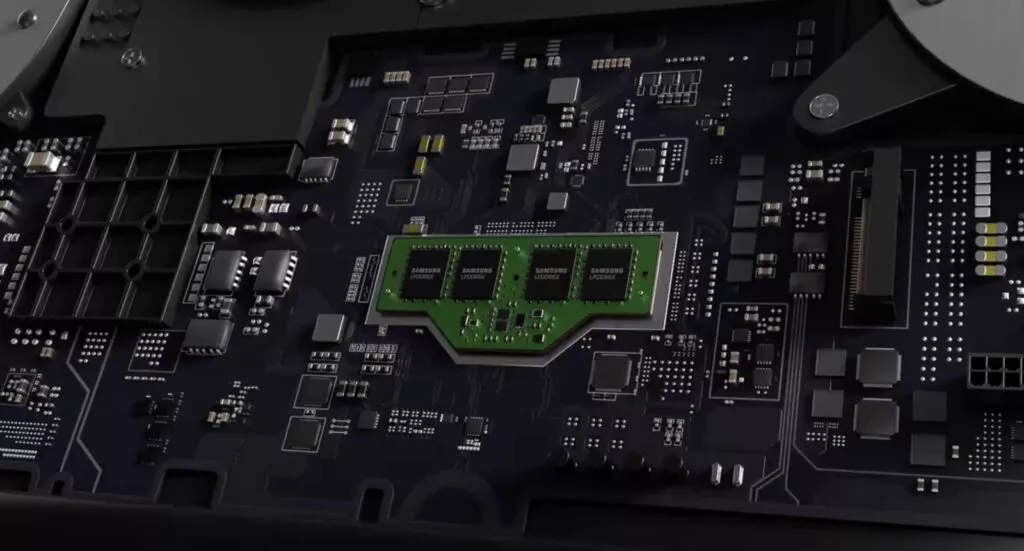
While the advantages of CAMM make it a no-brainer, its adoption won’t happen overnight. The transition is likely to be gradual, with both memory types coexisting in systems where they make the most sense, initially targeting gaming laptops and mobile workstations. A good example of this is Dell’s Precision 7670 laptop, which offers users the choice to select between SO-DIMM or CAMM.
Additionally, there is a major drawback to the standard as well. Unlike SO-DIMM, which usually offers dual slots, CAMM modules typically come as single pieces. Therefore, upgrading your laptop means that you will have to dispose of the previous RAM module.





