RAM Buying Guide: How To Pick The Right RAM For You?
When building or upgrading a PC, selecting the right RAM and setup is crucial. Unfortunately, many users unfamiliar with complex terminologies often end up with a system where RAM becomes a limiting factor in overall performance. Therefore, here is a comprehensive buying guide covering everything you need to know before purchasing RAM.
What is RAM?
To put things into perspective, Random Access Memory, or RAM, acts as a temporary storage hub for the operating system, offering fast data speeds. This makes it an ideal choice for current applications, processes, and programs.
To put it simply, consider your PC as a desk with cabinets. While the processor permanently stores data in the cabinets, it keeps frequently accessed information on the desk for quick retrieval. In this analogy, the desk represents the RAM, allowing the processor to store information quickly but temporarily.
Types of RAM
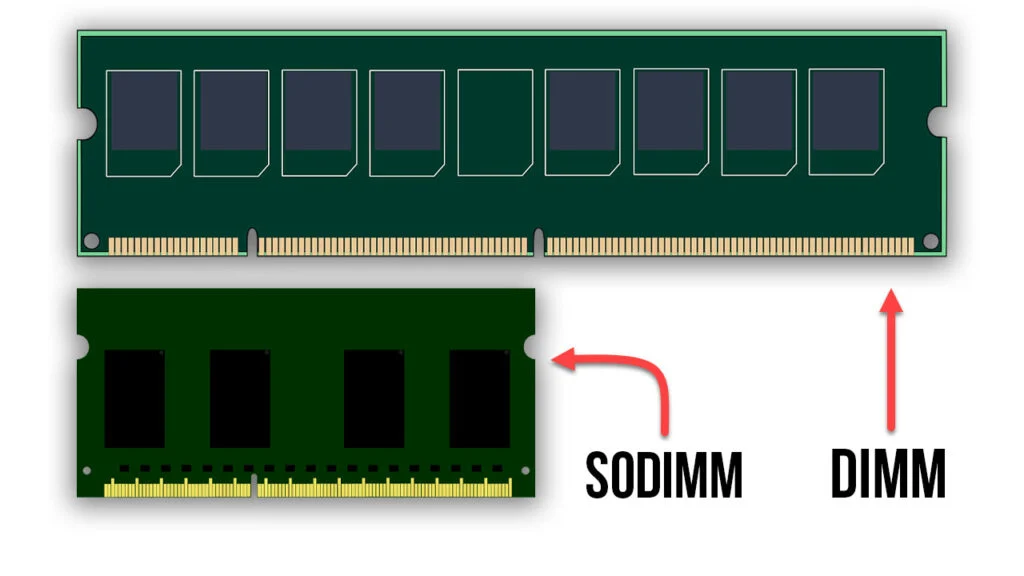
RAM comes in two configurations: DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) for desktops and servers and SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM) for laptops and compact computers. Despite sharing a common name, these form factors are not interchangeable. Therefore, inserting a DIMM stick into a SO-DIMM slot, or vice versa, will not work.
Different form factors
Since RAM speed directly impacts a system’s performance, let’s start with different form factors. You might have heard the terms DDR3 or DDR4, but what do they mean? In short, Double Data Rate (DDR) is the technology underlying RAM, indicating two transfers per clock cycle. As technology evolved, newer RAM versions emerged, called DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and so on. Currently, both DDR4 and DDR5 are in operation.
DDR4 vs DDR5? What is the difference?
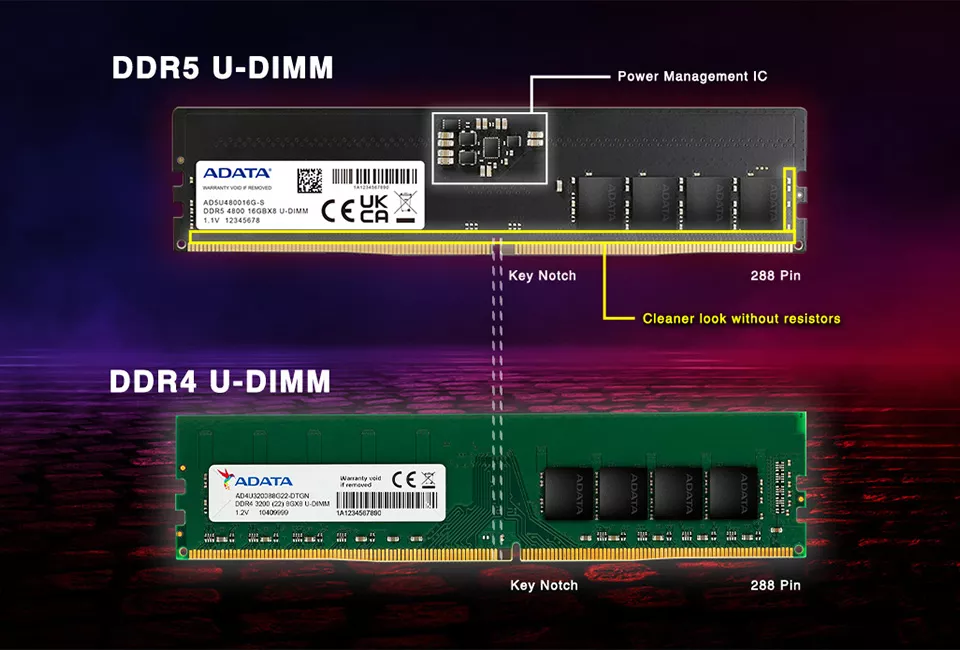
Choosing between DDR4 and DDR5 is perhaps the most important decision of them all. As the names suggest, DDR5 offers superior speed due to its architectural reconfiguration. Additionally, unlike DDR4’s single 64-bit channel, DDR5 DIMMs feature two independent 32-bit channels, effectively doubling the burst length from 8 to 16 bytes. This fundamental change results in significantly improved memory performance.
Moreover, DDR5 operates at a lower voltage of 1.1V compared to DDR4’s 1.2V, making it more power-efficient—a factor that can add up over years of PC use. However, it’s crucial to note that actual operating voltages may vary depending on the brand.
| Features | DDR4 RAM | DDR5 RAM |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Speed | 1600MHz – 3200MHz | 4800MHz – 6400MHz |
| Die Density | 16Gb SDP – 64GB DIMMs | 64Gb SDP – 256GB DIMMs |
| Voltage | 1.2V | 1.1V |
Which one should you buy?
While DDR5’s advantages may make it seem like the superior choice, the decision depends on your specific PC requirements. DDR4, being older, enjoys widespread support, spanning from the latest Intel 14th Gen processors to those launched in 2014. In contrast, DDR5 is exclusive to Intel’s 12th- and 13th-generation CPUs, with the AMD Ryzen 7000 being the only desktop CPU requiring DDR5. As a result, if you have an older processor, DDR5 becomes unsuitable, and you should opt for faster DDR4 RAM instead.
Capacity?
The next crucial step in choosing RAM is determining the capacity, which plays a vital role depending on your workflow. Different RAM capacities include:
- 8GB: Suitable for building an entry-level PC, especially if you don’t plan to play AAA games.
- 16GB: A sweet spot for users who want to game and multitask in their daily workflow.
- 32GB and above: Ideal for professionals and high-end gamers with demanding tasks and resource-intensive applications.
Which speed of RAM should you go for?
Before delving into the explanation, it’s crucial to check the maximum RAM speed supported by your motherboard. You can find this information in your motherboard manual or by using third-party software like CPU-Z.
If you plan on opting for DDR4, consider purchasing RAM sticks with speeds exceeding 3,000 MHz. This ensures your system can handle both gaming and heavy workloads effectively.
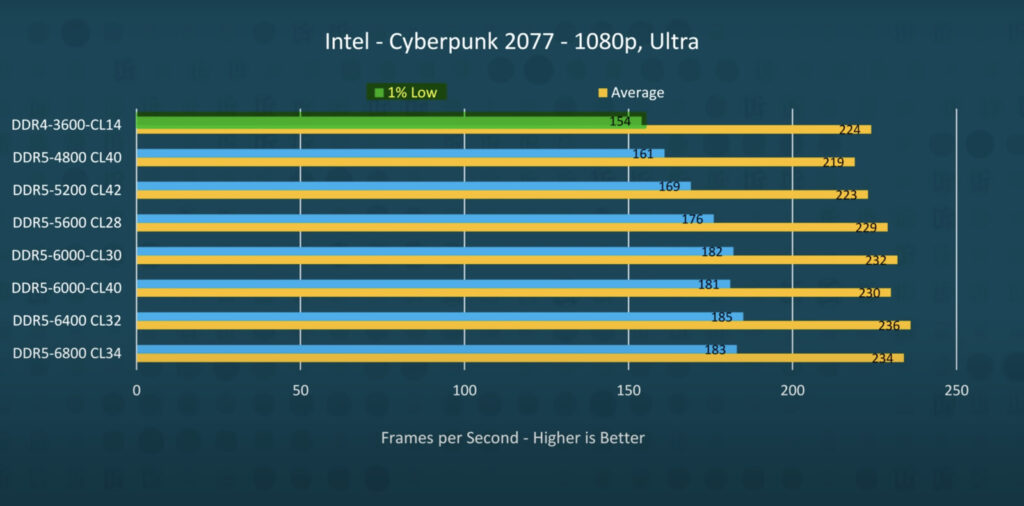
On the other hand, DDR5 offers speeds in the 4800 MHz – 6400 MHz range. However, users should not spend more to get the fastest stick, as the performance difference isn’t proportional. As a result, the lowest standard DDR5 RAM, i.e., 4800 MHz, provides the best value for money. However, it is important to note that DDR5 is inherently more expensive than DDR4.
Always use multiple channels

Every motherboard has 2-4 RAM slots, with a single stick of RAM representing a single channel while two sticks represent a dual channel. The choice between them depends on your budget and use case.
Suppose you plan on installing 16GB of RAM. In this case, choosing between a single 16GB stick might seem economical, as two separate sticks will be more expensive. However, a dual-channel configuration allows the processor to access both memories simultaneously, providing about 20%-25% more performance.
Furthermore, it is important to note that while dual-channel memory is preferred, you should not combine two different memory sticks, even from the same vendor and product line. Always use identical sticks to maintain stability.
Recommendations
While we recommend conducting your research, considering every motherboard supports a different standard, some of the best RAM sticks currently on the market include:






