How To Check DNS Records Using Basic Nslookup Command Examples
 Short Bytes: Nslookup command can be very handy in finding out different kinds of information using DNS queries like mail exchange server information, authoritative information, doing reverse lookup etc. Nslookup can be run in the command prompt on Windows very easily.
Short Bytes: Nslookup command can be very handy in finding out different kinds of information using DNS queries like mail exchange server information, authoritative information, doing reverse lookup etc. Nslookup can be run in the command prompt on Windows very easily.
In simple terms, Nslookup queries a local or the remote DNS servers to dig out information about the requested domain. You can also use many variants of this command on CMD to find out more and learn more such as knowing about the mail servers, FQDN, IP address etc.
If you are interested in knowing more about DNS, here is what we recommend you: How DNS works?
Now, we are going to see how to use basic Nslookup command to query more about domain names.
-
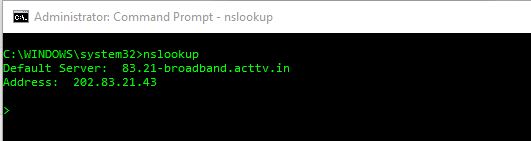
Nslookup to know your default DNS server and IP address
Just type nslookup in you command prompt and you will get your default DNS server and its IP address:
-
Nslookup for any web servers IP address
Let’s say I want to know the IP address of Microsoft’s web servers. So just nslookup microsoft.com in you command prompt and you will get the DNS server name and its IP address:
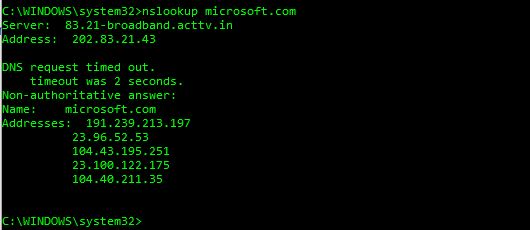
In the above screen, you can see that there is a term called Non-authoritative answer. This answer is shown when the reply comes from a source which is not considered authoritative for the domain which it’s returning a record for.
For example, in the above query, the response is coming from my default DNS server which would come as non-authoritative because it is not listed in the list of nameservers for microsoft.com.
-
Different types of Nslookup commands
In the table below, I am going to list out some of the famous Nslookup commands which can be used for different purposes. I will also list out a few examples in the beginning and then I will finally list out those all in a table at the end.
Nslookup example with a parameter:
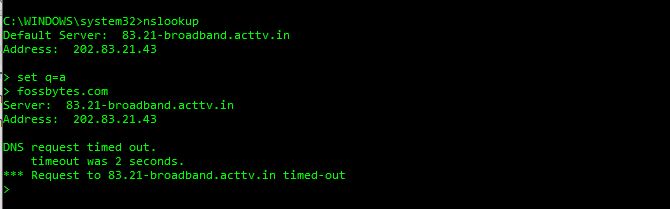
Let’s understand the above Nslookup query first.
In the above query, the command follows this way:
- nslookup <Enter>
- > set q=a <Enter>
- > fossbytes.com <Enter>
Now let’s see how to execute by setting different kinds of parameters (the list of which will be given in the table in the end) and do various DNS queries.
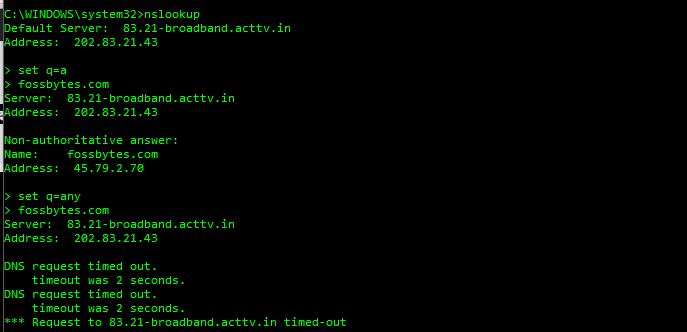
Now if you compare the above image to its previous image, you can see that I have continued setting the different type of DNS queries on the same screen in continuation.
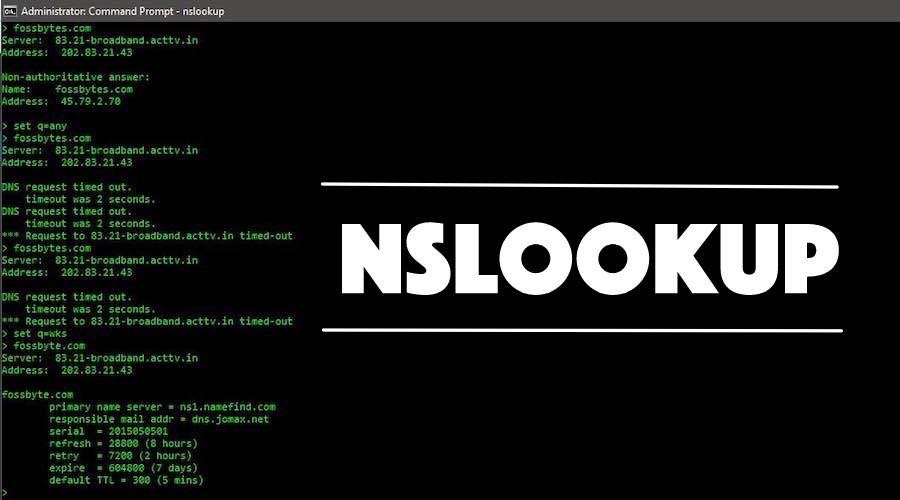
In the following image, I am continuing my different types of queries in the same screen and this time I am querying for Well-Known Service (WKS) for our website fossbytes.com.
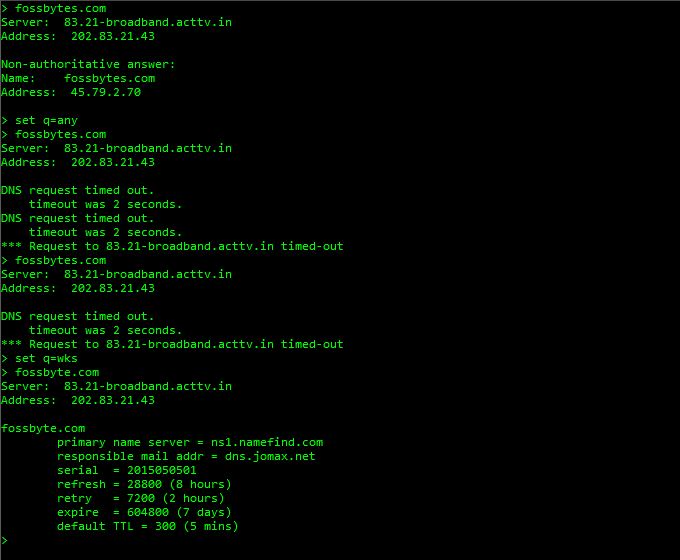
This query is showing me some more data about fossBytes like primary server name, refresh time, default TTL, mail address etc.
You can also perform many other queries the same way for which I am providing a table below:
| Set queries | Description |
| set q=a | To know the IP address |
| set q=any | To know all types of data |
| set q=CNAME | To know the Canonical name |
| set q=MB | To know the Mailbox domain name |
| set q=MX | To know about the mail exchange server |
| set q=SOA | To know about the Start-Of-Authority of a DNS Zone |
| set q=WKS | To know about the Well Known service |
Also Read: How To Find And Kill A Remote Connecting Malware On Windows 10






