How Do Electric Cars Work? Electric Motors And Batteries Explained

If you want to learn “How do electric cars work?”, you’ve come to the right place. Electric cars are booming nowadays. These eco-friendly and pollution-free cars are the future.
All major automakers are investing in electric vehicles. Just like every new piece of technology, people want to know how electric cars work.
What’s surprising is that electric car technology isn’t new at all. They came into existence before the internal combustion vehicles. The first successful electric car was made in the 19th century by Robert Anderson, an English inventor. It was a fairly basic car, and since then, modern electric vehicles have become a lot more sophisticated.
Modern electric cars like the Tesla Model S are super fast. With an acceleration of 0-60 mph in 2.3 seconds, one might think that these cars must be powered by dark magic. However, that’s not the case. You’ll understand this as we proceed.
How Much CO2 Can an Electric Car Save?
One of the biggest reasons people consider EVs is that they are better for the environment, with lower emissions than petrol and diesel cars. But are they better? While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, their overall environmental impact depends on how electricity is generated. Since there’s no way for us to know how electricity at your home is generated, an emissions calculator can help estimate how much carbon dioxide an electric car can save over a conventional vehicle.
Such tools take into account metrics such as annual driving distance, fuel type, and the location of electricity generation. For example, if the electricity reaching your home is coming primarily from a coal plant, then the CO2 emissions of charging an EV will be similar to just driving a gas car.
Ev Emissions Calculator by CalculateYogi
How Do Electric Cars Work?
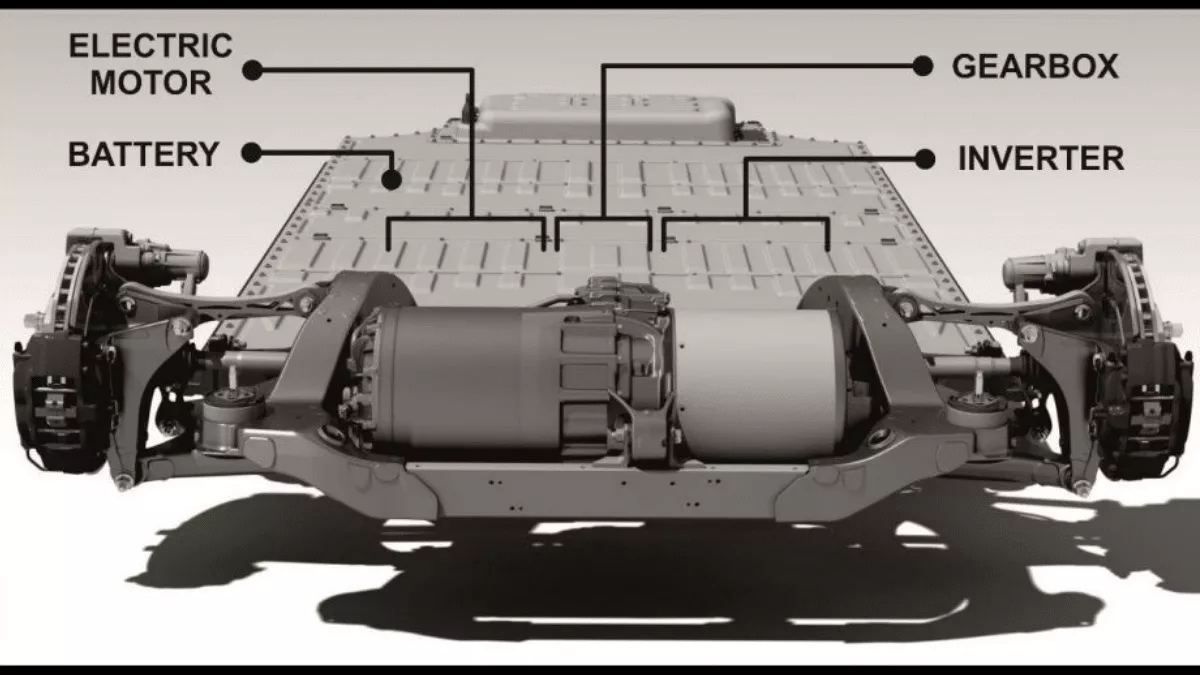
An electric car consists of three main parts:
- an electric battery (usually a lithium-ion)
- electric motor
- inverter.
Batteries store electric energy and produce Direct Current (DC). The inverter converts the DC supply from the battery to the AC and transfers it to the motor. After that, the motor spins the wheels via a gearbox and moves the car forward.
In simple words, the electric motor works as the engine, and the battery serves as the fuel or power source.
Now, let us understand the different parts of an electric car, and how do they work?
1. Electric Car Motor: What Is It And How Does It Work?
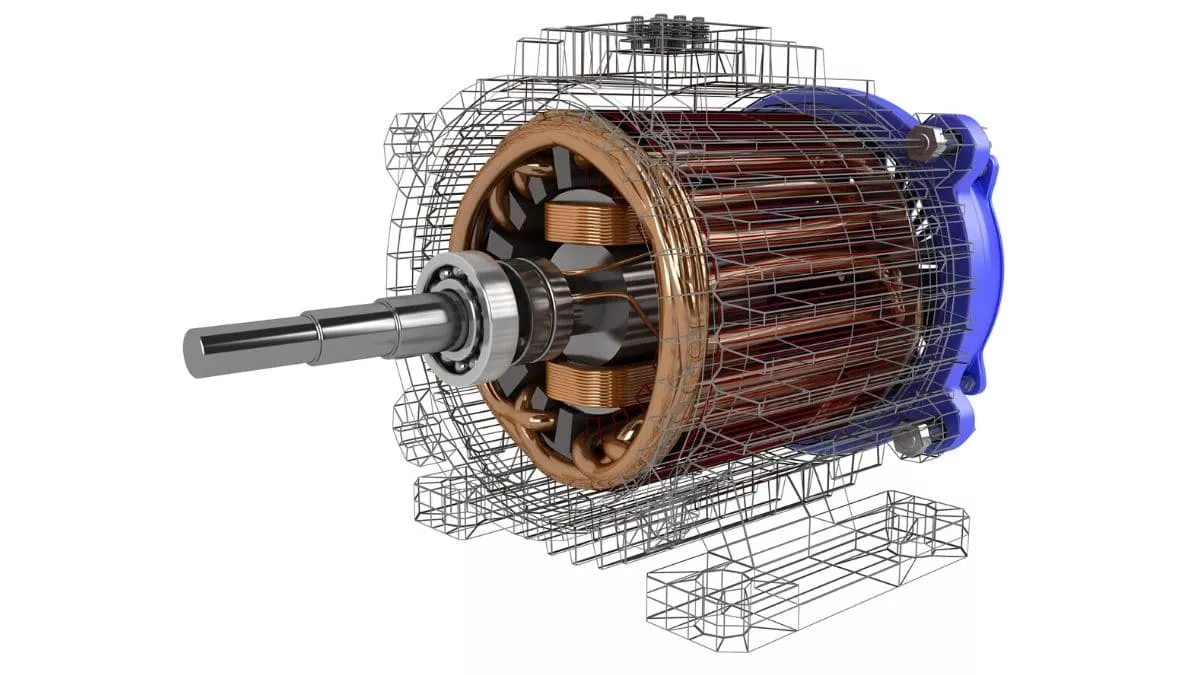
The motor used in electric cars is the AC induction motor. Let me remind you, the induction motor, along with the RMF (Rotating Magnetic Field), was invented by the great scientist Nikola Tesla in 1887.
The electric motor has two parts: a stator and a rotor. The stator is the stationary part that generates the Rotating Magnetic Field or RMF. Meanwhile, the rotor is the moving part that spins under the effect of RMF.
When the Alternating Current or AC passes through the stator, it creates an RMF, which causes the rotor to spin. The rotor is connected to a transmission, which turns the wheels and moves the car forward.
2. Electric Car Batteries: What is Their Function?
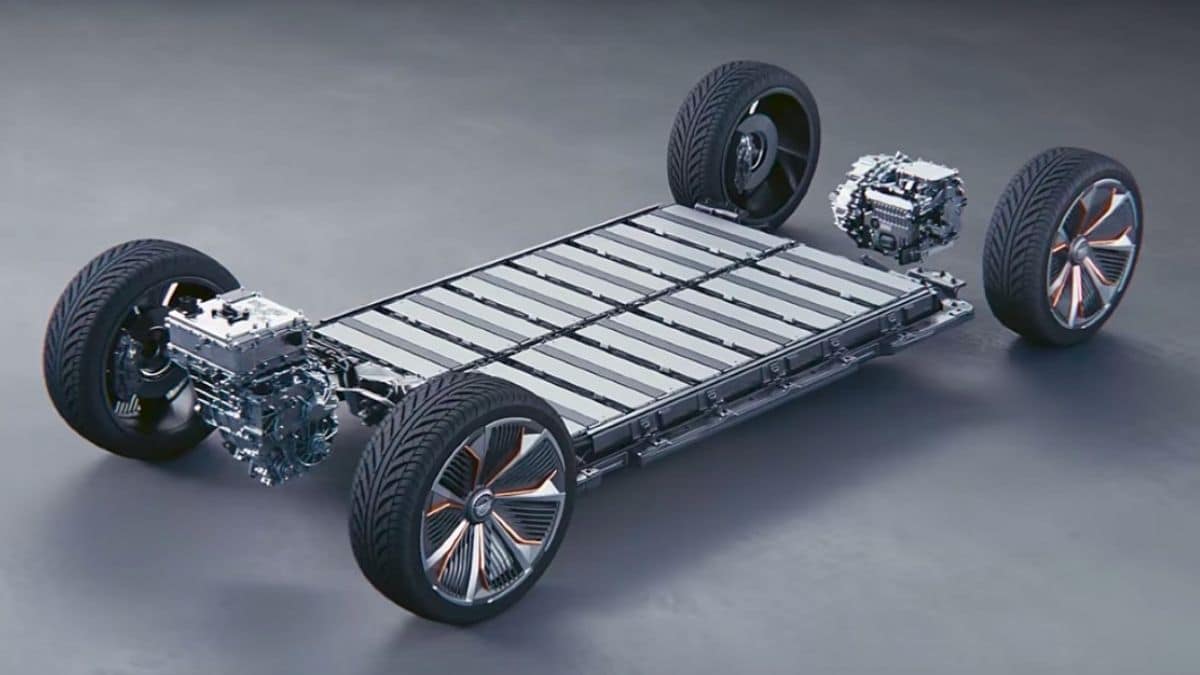

Electric car batteries are generally made up of lithium-ion cells because of their high energy density. Similar to other batteries, these also contain a cathode, an anode together known as electrodes, and an electrolyte.
Lithium-ion batteries can be recharged several times. Each time the battery recharges and discharges, it is known as a Charge cycle. Electric car batteries have a limited number of charge cycles.
How Does A Lithium Ion Battery Work In Electric Cars?
When the battery is in use, the lithium ions flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. When the battery charges, the lithium ions move away from the positive electrode towards the negative one and stay there.
When the battery of an electric car charges for the first time, the electrodes react with the electrolyte to form an initial SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interface) layer.
This reduces the battery capacity by a small amount, and the process is called Formation loss. However, this initial formation of the SEI layer facilitates the battery to get charged and discharged thousands of times without the electrode reacting with electrolytes.
Let’s Understand Better Through Tesla Model 3 Battery

The 2020 Tesla Model 3 is designed to have more than 1,300 charging cycles. This means that the Model 3 can easily travel 300,000 miles before it starts to show any significant signs of battery degradation.
The chemical composition of electric car batteries also keeps changing as we move ahead in time. Currently, Tesla uses a combination of Nickle-Manganese-Cobalt in the ratio of 8:1:1. The most expensive component in this combination is Cobalt.
And according to a recent report, Tesla plans to further reduce the proportion of Cobalt in its future electric car batteries. This will help make the upcoming EVs very affordable.
Where Are Batteries Installed In Electric Cars?
Most lithium-ion battery packs weigh a significant amount. The batteries are usually placed underneath the car’s floor.
The heavy battery packs increase the weight of the electric vehicle significantly, but it also provides them with a very low center of gravity. Which, in turn, provides them with a very planted ride.
However, in some electric cars, batteries are also installed under the front bonnet.
3. Inverter In Electric Cars
As mentioned previously, the inverter in electric cars converts the DC power coming from the battery into the AC and supplies it to the induction motor. Additionally, it can also vary the amplitude of the AC power, which in turn controls the electric motor.

The inverter is significantly responsible for controlling the speed of the vehicle. One can think of it as a throttle body. However, it functions in more ways than that.
How Do Regenerative Braking Work In Electric Cars?

Electric cars are highly efficient. Not only do they require less energy to move, but they also replenish the charge that they spend while driving via a process called Regen.
When the electric car is moving forward, the rotor speed is less than the RMF speed. However, during regen braking, the rotor speed becomes higher than the RMF speed, causing the motor to function as a generator and convert kinetic energy into electrical energy.
An opposing electromagnetic force acts on the rotor during this process, bringing the wheels and therefore the car to a halt. The inverter adjusts the power frequency and keeps the input RMF speed lower than the rotor speed.
While Regen is active, a substantial amount of electricity is generated in the stator coils. This electricity is added to the battery pack, increasing the overall range of the car.
Different Ways Of Using Regenerative Braking
Different electric cars use Regen differently. In cars like the Porsche Taycan, the regenerative braking works when you hit the brake pedals.
Whereas, in a Tesla, there’s a feature called single-pedal driving. Using which you can pretty much drive your car without using the brakes. In single-pedal driving mode, your car will accelerate normally but as soon as you lift your foot off it, the electric motor will slow you down leaving your brakes unused.
The Future Of Electric Vehicles
CNBC reported that out of the 5.1 million cars sold globally, around two million were electric cars. These were majorly sold in China, the U.S., and Europe.
According to several experts, the share of electric vehicles will continue to rise as battery technology and supporting infrastructure develops.
Furthermore, several Asian markets, including India, still remain scarcely populated by EVs.
The few electric cars launched in the region are able to perform well in terms of sales. However, surrounding charging infrastructure in the region needs to be developed before the mass adoption of EVs can take place in these regions.






