Everything About AMD’s Ryzen Naming Scheme: Laptops And Desktops

AMD’s comeback in recent years has been nothing short of amazing, with people finally having a choice among laptop/desktop processors. However, similar to Intel, the company’s naming scheme has left much to be desired with its confusing names and numbers.
Moreover, the fact that AMD uses different naming schemes for its desktop and laptop processors means an average user must invest a lot of time in research. Therefore, here is everything you need to know about AMD’s naming scheme.
AMD’s Mobile Processors for Laptops
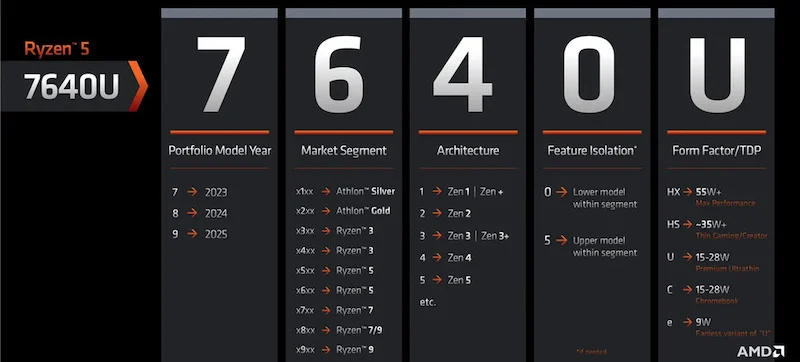
To better understand the naming scheme better, let’s consider the example of the AMD Ryzen 5 7640U. At first glance, the string of numbers might appear overwhelming, but each holds a specific meaning.
1. Brand Modifier
AMD’s branding is relatively straightforward, with higher numbers indicating better performance. For instance, the Ryzen 5 series outperforms the Ryzen 7 series, and so forth.
2. Model Year
The first number of the laptop processor signifies the model year. In the case of our example, the Ryzen 5 7640U, the “7” represents the model, indicating that the processor was launched in 2023. Consequently, significant generations will bear the number 8 for 2024 and 9 for 2025.
3. Segment
Similar to brand modifiers, the second digit of the name, in our case, “6,” represents the CPU’s segment. However, AMD includes a wide spectrum of processors in this number, ranging from Athlon Silver and Gold to the Ryzen series. Other numbers in the series include:
- 1 represents the Athlon Silver series.
- 2 represents the Athlon Gold series.
- 3 and 4 denote the Ryzen 3 series.
- 5 and 6 indicate the Ryzen 5 series.
- 7 represents the Ryzen 7 series.
- 8 represents the Ryzen 8 series.
- 9 represents the Ryzen 9 series.
4. Architecture

Arguably the most crucial aspect, the third digit signifies the architecture of the chip. But you may wonder, why is architecture important? The answer lies in performance and efficiency. The architecture reflects the manufacturing process of an AMD chip. For instance, the 7000 series operates on TSMC’s latest 5nm process, rendering it nearly 30% faster than its predecessor.
Within the name, the digit following the market segment denotes the Zen microarchitecture version, spanning from 1 to 5. In our example, the “4” in the Ryzen 5 7640U signifies it operates on the latest Zen 4 architecture.
- 1 denotes Zen 1 or Zen+.
- 2 signifies Zen 2.
- 3 represents Zen 3 or Zen 3+.
- 4 indicates Zen 4.
5. Feature Isolation
While not as important, the final digit in the processor’s name identifies additional attributes like Thunderbolt support or USB variants. However, it is important to note that these features typically do not significantly impact day-to-day processor usage.
AMD’s Desktop Processors
Compared to AMD’s laptop chips, where each number within the name carries a different meaning, understanding the company’s desktop processors is relatively simpler. However, before delving into the explanation, it is important to divide AMD’s desktop processors into three SKUs. The first, Athlon, serves as an entry-level CPU for routine tasks, while Ryzen caters to more performance-oriented users. Lastly, AMD Threadripper is designed for server-centric tasks and can include over 100 cores.
However, to understand the naming scheme, consider the example of the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D. The name comprises of:
1. Brand Modifier
AMD’s desktop chips follow the same approach as the laptop processors, with a higher number indicating the better chip.
2. Generation and Architecture of CPU
As previously mentioned, the CPU’s generation is among its most important aspects. Fortunately, the first number in the name denotes exactly that. However, the generational naming slightly differs from that of laptop chips. In desktop chips, the first number indicates both the generation and architecture of the chip. Presently, “7” denotes the latest generation, representing the Zen 4 architecture.
3. SKU
The last three digits of the name represent a chip’s SKU. To better understand their significance, let’s compare our example, the Ryzen 9 7950X3D, with the Ryzen 9 7900X3D. Unlike laptop chips, the last three digits do not carry specific meanings; instead, a higher number simply indicates a superior processor. As a result, the Ryzen 9 7950X3D outperforms the Ryzen 9 7900X3D in terms of performance.
4. SKU Suffix
It’s no secret that AMD offers various iterations of a chip, each tailored to specific workflows. However, for users less familiar with tech, choosing the right chip might be challenging. This is where the significance of the last letter in the chip’s name becomes important, as it signifies the type of chip. SKU suffixes include:
- G: In earlier Ryzen CPU generations, ‘G’ indicated the inclusion of a dedicated graphics processor, as many chips lacked integrated graphics. However, in current iterations, all CPUs come equipped with integrated graphics, making the ‘G’ designation obsolete.
- F: Recently, the company introduced a new suffix with the 7000 series, indicating CPUs without an integrated GPU.
- X: This designation denotes a slightly better CPU in terms of clock speed and operating temperatures.
- X3D: In the Ryzen 5000 series, AMD introduced the new X3D technology, which layers an additional cache atop the CPU. This effectively doubles the L3 cache, resulting in heightened performance levels.