Wi-Fi 7 Explained: How Fast Is It? When Is It Coming?
Wi-Fi technology has evolved rapidly in the last few years, going from Wi-Fi 6 to 6E in a short time. Now, just as users are adapting to Wi-Fi 6E, its successor, Wi-Fi 7, is already on the horizon, promising faster speeds, reduced latency, and improved reliability. Here is everything you need to know about it.
What is Wi-Fi 7?
Dubbed IEEE 802.11be, the new Wi-Fi standard aims to redefine the digital landscape with enhanced bandwidth. This advancement translates to download speeds up to 4 times faster than those achievable with Wi-Fi 6E.
However, perhaps the biggest feature of the new standard lies in its ability to circumvent network congestion through advanced signal modulation techniques. But, you might wonder, weren’t these enhancements promised with Wi-Fi 6E as well? To understand this, let’s compare the two standards.
Wi-Fi 6E vs. Wi-Fi 7
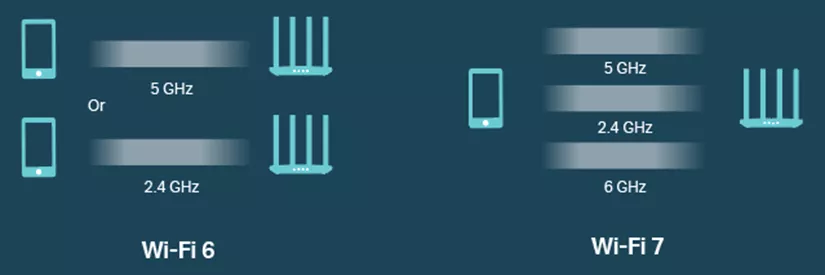
Although both standards operate on the 6GHz frequency, Wi-Fi 7 stands out as a significant leap forward. This is because, unlike Wi-Fi 6E, Wi-Fi 7 introduces wider channels, reaching up to 320 MHz. This substantial expansion directly boosts data transmission capacity.
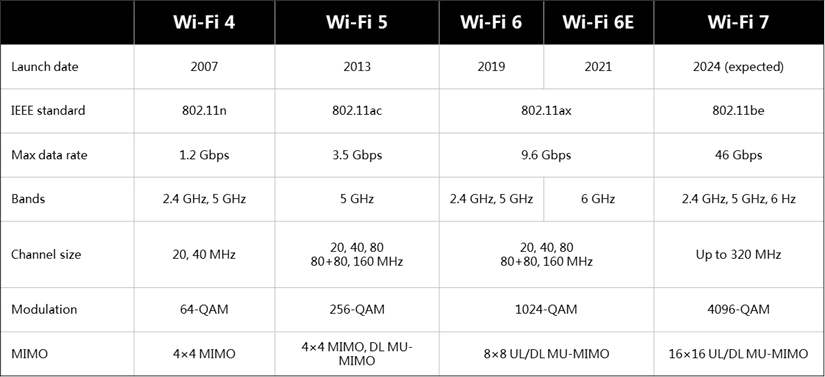
Another standout feature of Wi-Fi 7 is Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), which is essentially a way for analog signals to transmit digital information easily. Although previous Wi-Fi versions also supported QAM, Wi-Fi 7 takes it up a notch by adopting 4K-QAM, which significantly improves data-packing potential.
However, an important aspect to note is the inverse relationship between QAM and range: as QAM increases, the range decreases. Therefore, Wi-Fi 7 requires a stronger signal to maintain the same range.
Furthermore, unlike its predecessor, Wi-Fi 7’s Multi-Link Operation (MLO) tackles connectivity issues by enabling devices and routers to connect using multiple channels across different bands concurrently. This advancement could remove latency concerns by allowing routers to transmit data packets through various channels rather than relying on a single one. Additionally, the new routers can also optimize channel usage, adapting to varying conditions and potentially addressing range limitations.
Will it improve internet reliability?
When talking about a home Wi-Fi system, the biggest issue in wireless transmission is airtime allocation, which leads to delays when routers juggle multiple devices. To fix this issue, Wi-Fi 7 uses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) to optimize carrier waves and accommodate more data.
However, it is important to note that compatibility issues may arise when a Wi-Fi 7 router attempts to connect with unsupported devices. This is because a complete migration to the new standard is necessary to fully harness its capabilities.
Limitations of Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7, like any technological advancement, comes with its set of limitations. Presently, most devices are designed to support Wi-Fi 5 or 6, indicating that the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi 7 may take some time. Additionally, the fact that the IEEE has yet to adopt the new standard adds another layer of complexity since the Wi-Fi 7 routers available today may become outdated as the governing body establishes more rules and regulations. However, the Wi-Fi alliance has recently announced that they will finalize the standards by the end of Q1 2024.
Do devices already have Wi-Fi 7?
Despite Wi-Fi 7 not yet being formally embraced by the IEEE, some devices already offer support for the new standard. Qualcomm’s FastConnect 7800 chip stands as an example, although it necessitates updates from manufacturers for full integration. In terms of PCs, users interested in adopting Wi-Fi 7 will need to invest in compatible network cards to align with this new standard.
When talking about routers, there’s already a range of options available. This includes routers like the TP-Link Archer BE800, priced at $599, and the Netgear Orbi RBE973, which is considered one of the top mesh routers in the market but comes at a significant cost of $1,499.

How to check if your router supports the new standard?
If you’ve recently invested in a new router, there’s a possibility that it might already be Wi-Fi 7 compatible. To confirm its compatibility, visit the specification page of your specific router. Look for details mentioning support for IEEE 802.11be in the specifications.
Is it Time to Upgrade?
As the standard remains subject to potential changes, it might not be the best time to invest a substantial sum in upgrading your setup. Additionally, keep in mind that device manufacturers, such as Samsung, will need to roll out updates enabling Wi-Fi 7 on their devices. Therefore, even if you decide to upgrade your setup, you might not be able to take full advantage.